Quantitative research:
This method of research is used for: describing variables, to examine relationships among variables, to determine cause-and-effect interactions between variables. It is also a formal, objective, systematic process that numerical data are used to obtain information about the world. Quantitative research is usually made with using scientific methods that includes:
- The generation of models, theories and hypotheses
- The development of instruments and methods for measurement
- Experimental control and manipulation of variables
- Collection of empirical data
- Modeling and analysis of data
Pros and cons:
Pros:
- When the survey has a convenience sample (e.g. a mall intercept study), data can be gathered and analyzed quite quickly
- When the survey has a statistically valid random sample, the results from the sample can be generalized to the whole population only if the response rate is high enough.
- Surveys may provide reliable (i.e. repeatable) direction for planning programs and messages
- Surveys may be anonymous, this is useful for sensitive topics
- Like qualitative research methods, surveys may include visual material and can be used to pretest prototypes
- You can generalize your findings beyond your participant group.
Cons:
- They have limited ability to probe answers
- People who are willing to respond may share characteristics which don’t apply to the audience as a whole, creating a potential bias in the study
- They can cost a lot of money
Examples:
The top selling DVD of 2015 so far is Big hero 6, grossing $657 million worldwide. It won the Academy Award for Best Animated Feature and was nominated for an Annie Award for Best Animated Feature and a Golden Globe Award for Best Animated Feature Film.
 |
| Here is the worldwide sales for Big hero 6 |
 |
| Here are the sales for Big hero 6 |
Hits on a website- A hit is every file sent to a browser by a web server is an individual hit. A page view is when every time a visitor views a page on a website, regardless of how many hits are made.
 |
| This is the top 10 most popular websites. |
This is quantitative research because it is in these top 10 best website list, it is still quantitative research even though few numbers are seen. The most popular website is Google which is a search engine- allows users to search any world's information, including webpages, images, and videos. Offers and more unique features and search technology.
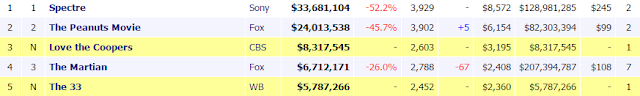
Box office sales- This is a business which is measured in terms of number of tickets sold or amount of money made by the ticket sales.
This is a quantitative research because its showing the figures of the box office top selling box office film. The top selling box office film of 2015 so far is 'Specter' its weekend gross reached $33,681,104 and its total gross is $128,981,285.
Qualitative research:
This method of research is a "primary exploratory research" that is used for gaining an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. It also provides insights into the problem or helps to develop ideas or hypotheses for potential quantitative research.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- It is dynamic, flexible
- Has depth understanding
- Helps customers creativity
- Smaller sample size: speedier results and costs less
- Penetrates rationalized, superficial responses
- formative creative ideas can be evaluated
- Richer source of ideas for marketing & creative teams
Cons:
- Responses aren't measured, also not statistically representative
- Depends on interviewer skills, orientation & interpretation
- Can't be repeated as easily with exactly replicable & this comparable results as quantitative research
- Requires trust in interviewer’s ability to draw (unseen) data together
- Smaller sample sometimes necessitates follow on larger quantitative sample for more controversial marketing decisions
- Dependent on interviewer skills & experience
- Interviewer involved requires particular skills/ experience in introducing such material & interpreting responses given
- "Less accessible" data mix for clients
Examples:
Game reviews-
Game reviews-
Attitudes to media products- Dictionary of business terms for attitudes- mental position or emotional feelings about products, services, companies, ideas, issues, or institutions. Attitudes are changed by demographics, social values, and personality.
 |
| This is the post the women posted which led to her being arrested |
also many other people have commented their opinions on this post.
Discussion- This is the opportunity to highlight how your research reflects, differs from and extends current knowledge of the area in which you have chosen to carry out research. This section is the chance to demonstrate exactly what you know about this topic by interpreting your findings and outlining what they mean. At the end of the discussion you should have discussed all of the results that you found and provided an explanation for your findings. For example in an interview for say a game idea you will have discuss the different ideas that you have and make it detailed and at the end the listeners can give their opinions on your idea.
Methods and sources of research:
Secondary research:
This research is also known as 'desk research'. It involves the summary, collation and/or synthesis of existing research. A key area in secondary research is the full citation of original sources, mainly in the form of a complete listing or annotated listing. Secondary sources could include previous research reports, newspaper, magazine and journal content, and government and NGO statistics.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- It is easy to access
- can find it quickly
- Usually the only resource
Cons:
- May not have all the information needed
- The found information might be out of date
- Not all of the data found will be correct unless you find it in an old book or it comes from the main source.
Examples:
Newspapers- Newspapers are good for research because it provides: news of the day, information about local events, first-hand accounts of events, coverage of state and local governments, obituaries and other information about local residents, editorials relating to state and local events and archives of past newspapers.
 |
| This is a news article about how games are not causing us to be violent |
This is secondary research because its a newspaper article about how games are not making gamers to become move violent. If someone wanted to research gaming addiction and weather or not it causes violence they could read this and also one that says it does then come up with a conclusion themselves.
Books- Textbooks can give you an introduction, background, and basic information on a topic. They generally present either summaries of a wide range topics and textbooks provide good background information and offer an excellent starting point for more in-depth research. Textbooks would be a great place to start if you need to know background/overview information and information that isn't rapidly changing.
Ratings- A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality (as with a critic rating a novel), quantity (as with an athlete being rated by his or her statistics), or some combination of both.
This is secondary research because it is ratings of most watch TV programs in UK and shows that EastEnders is the most watched. This is good for if someone wanted to research about popular TV shows in the UK or compare them with other shows.
Primary research:
This is research where you go out and find your own information on the subject you want to research instead of looking at someone else's which is secondary. There are multiple ways to do your own research like; questionnaires, market research, experiments, observations an discussion
Questionnaires- This is a list of a research or survey questions asked to respondents and designed to get extract specific information. It serves four basic purposes:
For example if you are at a restaurant they might ask you to fill out a questionnaire about the service or food to help them to know where they went wrong and what they are doing right.
Another example is a questionnaire at college or school where they may ask you about the lessons and college/school all together to get information about what they may need to do o make it better or know what the students think.
A final example for this is that you might get stopped outside shops in town/city centers to answer random questions about a specific topic like someone trying to sell a broadband network may ask you about your current one.
Surveys- Surveys are a way of gathering information from individuals and surveys have many purposes, which can be conducted in many ways. Surveys may be conducted to gather information through a printed questionnaire, over the telephone, by mail, in person, by diskette, or on the web. This information is collected through use of standardized procedures so that every participant is asked the same questions in the same way. It involves asking people for information in some structured format. Depending on what is being analyzed, the participants being surveyed may be representing themselves, their employer, or some organization to which they belong.
For example a patient at a hospital may take a survey to give information about their health and contact details to help the doctors have an idea about what they can and cant give to that patient and how to get in contact with them.
Another example is self assessment forms which can collect information about each employee, student or who ever takes this survey to help them get better, succeed or other which is to do with the survey.
A final example is job applications which gives the employer information about the person wanting to apply for the job and this wil help them decide who is right for the job and make sure they are the best choice.
Observations- This is when you observe or closely monitor someone or something. Observation is good for research because they provide researchers with ways to check for nonverbal expression of feelings, determine who interacts with whom, grasp how participants communicate with each other, and check for how much time is spent on various activities. Participant observation allows researchers to check definitions of terms that participants use in interviews, observe events that informants may be unable or unwilling to share when doing so would be impolitic, impolite, or insensitive, and observe situations informants have described in interviews, thereby making them aware of distortions or inaccuracies in description provided by those informants.
For example An audience member watching a movie play on the big screen to fully understand the story of the movie and to know if they like this movie o not.
Another example is a news reporter observing their assigned location or topic of what they have to look into for the news.
A final example is a game designer who needs to observe gamers or their target audience to find out what type of games are popular or what they like to play to help them decide what game to make.
Data gathering agencies:
Broadcasters’ Audience Research Board (BARB)- This is an organisation which compiles audience measurement and television ratings in the United Kingdom. It was created in 1981 to replace a previous systems whereby ITV ratings were compiled by JICTAR (Joint Industry Committee for Television Audience Research), whilst the BBC did their own audience research.
Research that they have done is Top 10 shows for every channel
This shows that 'Ghost Adventures' is the most watched show on the channel 'Really', and with all the other channels top ten shows, BARB can find out which shows are most popular and what people like best.
Another example of BARB and what they do is that they do the top 30 shows too
This shows that 'The Big Bang Theory' is the most watched on this list and EastEnders is the least watched. Also the audience is a big part in this BARB research and needs as many as possible to be able to get specific/good enough research/findings.
A third example is that BARB has now added online and catch-up to the ratings.
This shows that now they can have a clearer understanding of the nations viewing habits and will know what most the population likes to watch, also they have more information and can do more research like what people watch online.
Radio Joint Audience Research Ltd (RAJAR)- RAJAR is responsible for setting the research specification, the awarding of the research contracts to third party suppliers and the overall quality control , management and delivery of the service. The day to day operations are overseen by the Chief Executive and Research Director. The company is jointly owned by the BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation) and by the Radio Centre (the trade body representing the vast majority of Commercial Radio stations in the UK).
An Example of their research is that they keep track of the radio stations.
This is an example of how they keep track of the research like their names and how popular they are.
Purposes of research:
Audience research:
This is defined as any communication research that is conducted on specific audience segments to collect information about their attitudes, knowledge,interests, preferences, or behaviors with respect to prevention issues
Pros and cons:
Pros:
Examples:
Audience Profiling:
This is finding out the profile of your audience before hand so that you can put across your message to the right people in the most effective way to create the best result. It might include details like age, sex, educational qualification, work experience, financial background, field of work, interests, mood, orientation, bias, food habits, religious background, physique, health condition etc.
Age: Tv shows are a good example of this as all shows are aimed at a specific age audience. for example 'spongebob squarepants' is mainly aimed at very young kids to about 12 year olds due to it being a fun cartoon that can help them learn or just make them laugh and enjoy. Also the tv show 'Mrs Browns boys' is aimed at 16 and over people as it is a comedy show that has swearing and with few adult comedy. Furthermore the shows on Disney channel like 'Wizards of Waverley place' are aimed at young people ages about 11 to about 17 years old.
Gender: Some tv shows are mainly aimed at a specific gender but the opposite gender that it isn't aimed at may like it. For example 'Formula 1' is a sporty racing show and the general gender that it is watched by/appealed to is males. A show that is generally watched by females is 'Say yes to the dress' this is a show about wedding dresses and women who watch it either like it for some of the drama that happens, for the dresses, or if they are getting married and want dress ideas.
Audience data- The fundamental evolution in display advertising, ushered in by real-time bidding (RTB) technology, is the concept of buying audiences as opposed to just inventory. They used to buy “audiences” by guessing about the characteristics of the visitors to a particular site or type of site. Now, you can pick and choose individuals by their characteristics regardless of where they happen to be on the web.
As you can see there are five main criteria by which you can judge the quality of audience data. On one end of the spectrum, you have data which are opaque, fragile and of questionable value. On the other end of the spectrum, data which are transparent, robust and of the highest value to both marketers and publishers. By diving into the nuts and bolts, I hope you will see why this is the case.
This study demonstrated that the value of an audience, particularly in a re-targeting context, is highest within the first 7 days. This makes a huge impact on both bidding strategy (bidding higher during that 7-day window and less afterwards), and more importantly, valuing the quality of the data. Once again, with first-party data (which typically powers re-targeting campaigns), you have the most insight into the age of an audience, and therefore have the most insight into its value.
demographics- Demographics are quantifiable characteristics of a given population. Demographic analysis can cover whole societies, or groups defined by criteria such as education, nationality, religion and ethnicity.
Gender- While the target market for a given product can include females and males, one gender may represent a larger share of a company's target market. Businesses can segment their markets by gender, and come up with variations of their products devoted to serving a specific gender or alter their marketing campaigns to appeal to the male or female segment.
Age- This plays an integral role in how companies promote their products online and offline. Segmenting your market by age often involves diversifying pricing and color options, and adjusting features to fit the anticipated needs and expectations of each age group A bookstore releasing a new decade-specific book written about growing up in the 1980's, might send a promotion to customers born in the 1980-s, for example.
Marital Status- A company might discover that married individuals are more willing to pay higher prices than single individuals, or that single customers purchase a certain product more frequently than married people. A jewelry store can target married customers with promotions for anniversary bands, for example, while targeting unmarried women with "right-hand" rings, which are often worn as a signal of independence.
Geo-demographics- Geo-demography includes the application of Geo-demographic classifications for business, social research and public policy but has a parallel history in academic research seeking to understand the processes by which settlements (notably, cities) evolve and neighborhoods are formed. Geo-demography is the study of people based on where they live. Geo-demographic systems estimate the most probable characteristics of people based on the pooled profile of all people living in a small area near a particular address.
ABS - Australia's National Statistical Agency- The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) is Australia’s national statistical agency. The ABS provides key statistics on a wide range of economic, environmental and social issues. The ABS also plays an important leadership and coordination role in relation to the statistical activities of other official bodies, both within Australia and internationally. The Census of Population and Housing is the largest statistical collection undertaken by the ABS and is conducted every 5 years. The last Census was in 2011.
Books- Textbooks can give you an introduction, background, and basic information on a topic. They generally present either summaries of a wide range topics and textbooks provide good background information and offer an excellent starting point for more in-depth research. Textbooks would be a great place to start if you need to know background/overview information and information that isn't rapidly changing.
Ratings- A rating is an evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality (as with a critic rating a novel), quantity (as with an athlete being rated by his or her statistics), or some combination of both.
This is secondary research because it is ratings of most watch TV programs in UK and shows that EastEnders is the most watched. This is good for if someone wanted to research about popular TV shows in the UK or compare them with other shows.
Primary research:
This is research where you go out and find your own information on the subject you want to research instead of looking at someone else's which is secondary. There are multiple ways to do your own research like; questionnaires, market research, experiments, observations an discussion
Questionnaires- This is a list of a research or survey questions asked to respondents and designed to get extract specific information. It serves four basic purposes:
- collect the appropriate data
- make data comparable and amenable to analysis
- minimize bias in formulating and asking questions
- to make questions engaging and varied.
For example if you are at a restaurant they might ask you to fill out a questionnaire about the service or food to help them to know where they went wrong and what they are doing right.
Another example is a questionnaire at college or school where they may ask you about the lessons and college/school all together to get information about what they may need to do o make it better or know what the students think.
A final example for this is that you might get stopped outside shops in town/city centers to answer random questions about a specific topic like someone trying to sell a broadband network may ask you about your current one.
Surveys- Surveys are a way of gathering information from individuals and surveys have many purposes, which can be conducted in many ways. Surveys may be conducted to gather information through a printed questionnaire, over the telephone, by mail, in person, by diskette, or on the web. This information is collected through use of standardized procedures so that every participant is asked the same questions in the same way. It involves asking people for information in some structured format. Depending on what is being analyzed, the participants being surveyed may be representing themselves, their employer, or some organization to which they belong.
For example a patient at a hospital may take a survey to give information about their health and contact details to help the doctors have an idea about what they can and cant give to that patient and how to get in contact with them.
Another example is self assessment forms which can collect information about each employee, student or who ever takes this survey to help them get better, succeed or other which is to do with the survey.
A final example is job applications which gives the employer information about the person wanting to apply for the job and this wil help them decide who is right for the job and make sure they are the best choice.
Observations- This is when you observe or closely monitor someone or something. Observation is good for research because they provide researchers with ways to check for nonverbal expression of feelings, determine who interacts with whom, grasp how participants communicate with each other, and check for how much time is spent on various activities. Participant observation allows researchers to check definitions of terms that participants use in interviews, observe events that informants may be unable or unwilling to share when doing so would be impolitic, impolite, or insensitive, and observe situations informants have described in interviews, thereby making them aware of distortions or inaccuracies in description provided by those informants.
For example An audience member watching a movie play on the big screen to fully understand the story of the movie and to know if they like this movie o not.
Another example is a news reporter observing their assigned location or topic of what they have to look into for the news.
A final example is a game designer who needs to observe gamers or their target audience to find out what type of games are popular or what they like to play to help them decide what game to make.
Data gathering agencies:
Broadcasters’ Audience Research Board (BARB)- This is an organisation which compiles audience measurement and television ratings in the United Kingdom. It was created in 1981 to replace a previous systems whereby ITV ratings were compiled by JICTAR (Joint Industry Committee for Television Audience Research), whilst the BBC did their own audience research.
Research that they have done is Top 10 shows for every channel
 |
| This is an example of a channel and its top 10 shows |
This shows that 'Ghost Adventures' is the most watched show on the channel 'Really', and with all the other channels top ten shows, BARB can find out which shows are most popular and what people like best.
Another example of BARB and what they do is that they do the top 30 shows too
 |
| This is the top 30 shows from a mixture of channels |
A third example is that BARB has now added online and catch-up to the ratings.
This shows that now they can have a clearer understanding of the nations viewing habits and will know what most the population likes to watch, also they have more information and can do more research like what people watch online.
Radio Joint Audience Research Ltd (RAJAR)- RAJAR is responsible for setting the research specification, the awarding of the research contracts to third party suppliers and the overall quality control , management and delivery of the service. The day to day operations are overseen by the Chief Executive and Research Director. The company is jointly owned by the BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation) and by the Radio Centre (the trade body representing the vast majority of Commercial Radio stations in the UK).
An Example of their research is that they keep track of the radio stations.
This is an example of how they keep track of the research like their names and how popular they are.
Purposes of research:
Audience research:
This is defined as any communication research that is conducted on specific audience segments to collect information about their attitudes, knowledge,interests, preferences, or behaviors with respect to prevention issues
Pros and cons:
Pros:
- Sending questionnaires through E-mail would be people who wouldn't have received on when giving them out by hand and would give more information.
- Good for collecting information to determine the different audiences.
Cons:
- Sending out by E-mail you wouldn't know who is replying.
- Evaluation and collecting data from teenagers and young adults will narrow down the sights a bit.
Examples:
Audience Profiling:
This is finding out the profile of your audience before hand so that you can put across your message to the right people in the most effective way to create the best result. It might include details like age, sex, educational qualification, work experience, financial background, field of work, interests, mood, orientation, bias, food habits, religious background, physique, health condition etc.
Age: Tv shows are a good example of this as all shows are aimed at a specific age audience. for example 'spongebob squarepants' is mainly aimed at very young kids to about 12 year olds due to it being a fun cartoon that can help them learn or just make them laugh and enjoy. Also the tv show 'Mrs Browns boys' is aimed at 16 and over people as it is a comedy show that has swearing and with few adult comedy. Furthermore the shows on Disney channel like 'Wizards of Waverley place' are aimed at young people ages about 11 to about 17 years old.
 |
| This is Mrs browns boys |
 |
| This is spongbob squarepants |
 |
| This is Wizards of Waverley place |
Gender: Some tv shows are mainly aimed at a specific gender but the opposite gender that it isn't aimed at may like it. For example 'Formula 1' is a sporty racing show and the general gender that it is watched by/appealed to is males. A show that is generally watched by females is 'Say yes to the dress' this is a show about wedding dresses and women who watch it either like it for some of the drama that happens, for the dresses, or if they are getting married and want dress ideas.
 |
| This is Say yes to the dress |
 |
| This is Formula 1 |
Audience data- The fundamental evolution in display advertising, ushered in by real-time bidding (RTB) technology, is the concept of buying audiences as opposed to just inventory. They used to buy “audiences” by guessing about the characteristics of the visitors to a particular site or type of site. Now, you can pick and choose individuals by their characteristics regardless of where they happen to be on the web.
As you can see there are five main criteria by which you can judge the quality of audience data. On one end of the spectrum, you have data which are opaque, fragile and of questionable value. On the other end of the spectrum, data which are transparent, robust and of the highest value to both marketers and publishers. By diving into the nuts and bolts, I hope you will see why this is the case.
This study demonstrated that the value of an audience, particularly in a re-targeting context, is highest within the first 7 days. This makes a huge impact on both bidding strategy (bidding higher during that 7-day window and less afterwards), and more importantly, valuing the quality of the data. Once again, with first-party data (which typically powers re-targeting campaigns), you have the most insight into the age of an audience, and therefore have the most insight into its value.
demographics- Demographics are quantifiable characteristics of a given population. Demographic analysis can cover whole societies, or groups defined by criteria such as education, nationality, religion and ethnicity.
Gender- While the target market for a given product can include females and males, one gender may represent a larger share of a company's target market. Businesses can segment their markets by gender, and come up with variations of their products devoted to serving a specific gender or alter their marketing campaigns to appeal to the male or female segment.
Age- This plays an integral role in how companies promote their products online and offline. Segmenting your market by age often involves diversifying pricing and color options, and adjusting features to fit the anticipated needs and expectations of each age group A bookstore releasing a new decade-specific book written about growing up in the 1980's, might send a promotion to customers born in the 1980-s, for example.
Marital Status- A company might discover that married individuals are more willing to pay higher prices than single individuals, or that single customers purchase a certain product more frequently than married people. A jewelry store can target married customers with promotions for anniversary bands, for example, while targeting unmarried women with "right-hand" rings, which are often worn as a signal of independence.
Geo-demographics- Geo-demography includes the application of Geo-demographic classifications for business, social research and public policy but has a parallel history in academic research seeking to understand the processes by which settlements (notably, cities) evolve and neighborhoods are formed. Geo-demography is the study of people based on where they live. Geo-demographic systems estimate the most probable characteristics of people based on the pooled profile of all people living in a small area near a particular address.
ABS - Australia's National Statistical Agency- The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) is Australia’s national statistical agency. The ABS provides key statistics on a wide range of economic, environmental and social issues. The ABS also plays an important leadership and coordination role in relation to the statistical activities of other official bodies, both within Australia and internationally. The Census of Population and Housing is the largest statistical collection undertaken by the ABS and is conducted every 5 years. The last Census was in 2011.
Bluewave Geographics- Bluewave Geographics is a provider of digital mapping and geographical analysis services to the market research and fieldwork sectors with experience in the areas of spatial analysis, mapping, geo-demographics, survey design and sampling.
A Landmark paper: the first step towards big data?- Read Peter Mouncey's blog piece regarding his selection of a landmark paper from the International Journal of Market Research archives: The utility to market research of the classification of residential neighbourhoods - Ken Baker, John Bermingham and Colin McDonald, BMRB (published in the Journal of the Market Research Society, Vol.39 No. 1, January 1997).
Market research:
Market research allows a company to discover who their target market is and what these consumers think about a product or service before it becomes available to the public. Market research may be conducted by the company itself or by a third-party company that specializes in market research. Test subjects are usually compensated with product samples and/or paid a small stipend for their time.
Pros and cons:
Pros:
- Surveys and polls are a known quantity. Those in the industry know how to ask the right question to assemble the necessary data, so it’s a comfortable, obvious way to mine thoughts and opinions.
- surveys and polls have been used as market research resources for decades, decades of data to compare results against.
- Everyone knows what “In a recent survey…”means, so traditional methods make it easier for researchers to explain exactly how they got their results. It’s a simple process of survey, subject, and response that can be tailored for just about any topic.
Cons:
- Users are progressing in the way they interact with technology and each other. We wrote about why landlines are inaccurate for market research in today’s world, as it has simply become outdated.
- Survey farms, in centralizing survey completion, and even fake data can result in skewed results that are unpredictable. Also participants sometimes simply tell survey-takers what they want to hear, so answers are heavily biased
- To get the most participants and statistical significance, organizations are having to spend money on incentives, as well as multiple survey phases, making the process extremely expensive.
Examples:
Competitor analysis- Competitor analysis in marketing and strategic management is an assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of current and potential competitors. This analysis provides both an offensive and defensive strategic context to identify opportunities and threats.
This is an example of a table that a business/company may use to see what the competitors progress is like compared to their own.
Product market- Product market is where goods and services produced by businesses are sold to households. The households use the income they receive from the sale of resources to purchase the products. The money they spend is returned to the businesses as revenue.
Broadband- This is a high-capacity transmission technique using a wide range of frequencies, which enables a large number of messages to be communicated simultaneously.
 |
| Broadband examples |
These are examples of the top broadband sellers of the UK.
Advertising effects- The success rate/influence on sales of a product, due to a specific event/action.
Public Service Announcements- Public service announcements, or PSAs, typically utilize negative advertising techniques for their shock value. Showing the gruesome results of the activity they are trying to stop is often a very powerful tool to reach the heart and mind of a consumer. Instead of focusing on the positives of avoiding an activity, the ads show what will result if someone does the activity. These ads can very powerful and, while younger viewers may initially pass them off and laugh, they do reach them at a deeper level.
Car Advertisement Examples- Car advertisements are another example of positive and negative advertising, often within the same ad. When competitors' cars are mentioned, they are always put in a negative light: the car gets poor gas mileage or the styling isn't elegant. The advertisement then shifts to the car it is trying to sell and a positive switch occurs. All of the good features about that model are discussed. This can have a powerful effect on consumers, and the information imparted typically sticks in consumers' minds.
Newer Positive Advertisements- A trend towards more positive advertisements is particularly evident in the beauty industry. One campaign of note would be Dove's campaign for young women to help boost their self-esteem. These commercials discuss the beauty of everyone and the importance of inner beauty, instead of directly pitching a product. The result is that brand is associated with trying to do good at a personal level, and this psychologically impacts the brand's market to buy the products to support these efforts.
Production research:
Placement media- This is an advertising technique used by companies to subtly promote their products through a non-traditional advertising technique, usually through appearances in film, television, or other media. Product placements are often initiated through an agreement between a product manufacturer and the media company in which the media company receives economic benefit. A company will often pay a fee to have their product used, displayed, or significantly featured in a movie or show.
Coca-Cola could pay a given fee to have the title character drinking a Coke, instead of a Pepsi beverage.
Toyota might pay to have one of the characters drive their newest automobile.
Through product placement, companies hope that moviegoers will take note of the products used by the characters, and therefore think more strongly about using the products themselves.
Technological resources- Technological resources are systems and tools required to effectively produce or create a product or service. These include energy, information, people, tools, machines, capital and time. Technological resources aid production processes and service delivery in companies and organizations.
Viability-
Working methods:
Research- The systematic investigation into and study of materials and sources in order to establish facts and reach new conclusions.
 |
| This is an example of an article that has done research |
This is a research article about different media technology and health and see if it effects our health.
Production- This is the action of making or manufacturing from components or raw materials, or the process of being so manufactured.








No comments:
Post a Comment